What Is Progesterone?
Pro-gestation hormone, often shortened to progesterone, is an anti-inflammatory hormone produced before ovulation to enhance the possibility of becoming pregnant. It has a calming, soothing effect, raises serotonin levels in women's brain, which helps cope with depression and insomnia. And, of course, progesterone is vital for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Unfortunately, though, a lot of women of postmenopausal age and kids suffer from a progesterone deficiency which may lead to many health problems, including infertility.
The Importance of Progesterone in Women's Life
The importance of progesterone should not be underestimated since it’s needed for all women to live a healthy life, maintain a hormone balance and prevent the risk of breast or reproductive cancers. Any significant deviation from the norm may result in a range of unpleasant symptoms caused by rapid estrogen dominance. Some of these symptoms, unfortunately, are even hard to tell from usual tiredness and stress that are present in our everyday life. A lot of the symptoms are very common to how women feel during menopause and when they suffer from PMS. Tiredness, irritation, anxiety, weight gain, bloating, depression, headaches are just a few of the issues women deal with when the progesterone levels drop, to say nothing of more serious problems like lack of a period, bodily malfunctions, and even cancer. Women with low progesterone are often prescribed to undergo a progesterone therapy as well as taking some progesterone pills or/and progesterone oil compounds.
(Check your progesterone level using progesterone test strips)
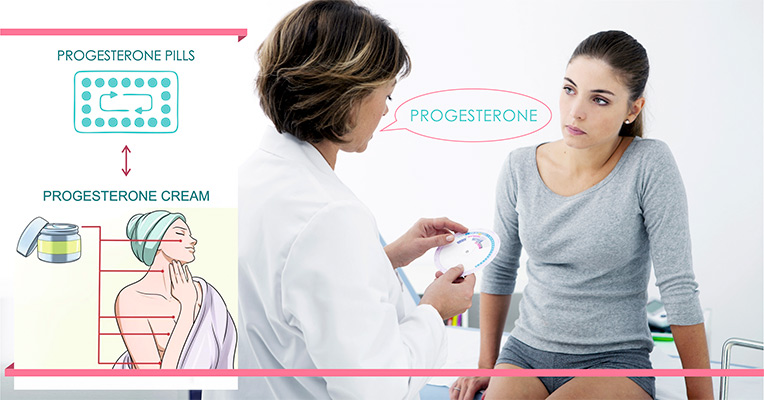
Progesterone and How It Is Commonly Used
Progesterone is found in many different forms and can be taken either by mouth if you’re prescribed to take progesterone pills, by intramuscular injections if the doctor recommends you to mix progesterone with the oil, or through the skin, if you choose to use progesterone cream. Commonly, progesterone creams are considered to be more effective since they don’t get lost through the liver and quickly get absorbed through the skin. Still, this is where the rule “the more the better” isn’t applied, for if you use more cream than recommended, you can achieve an effect opposed to the desired one and cause hormone imbalance. The compounds with the oils used on different women may also lead to very opposite reactions, therefore, the medication should be prescribed individually and, as we’ve mentioned above, by a professional. We will take a closer look at the treatments, including those that can be done in a natural way, further in the article. For now, let’s identify the common symptoms that tell of the progesterone deficiency and learn some basic causes that lead to the hormone imbalance.
(See the recommended aids: Progestelle Progesterone Oil, Emerita Pro-gest Cream, Life Extension Pregnenolone)
4 Common Low Progesterone Symptoms:
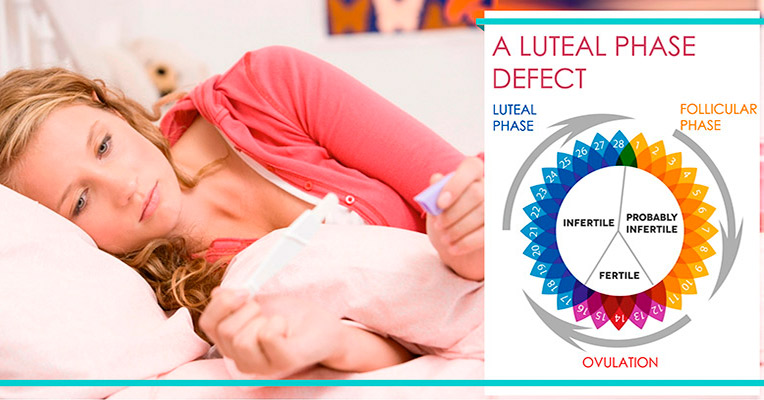
1) Short Luteal Phase
The luteal phase is the period between ovulation and the start of your period. It usually lasts for about 11 and 14 days starting with the formation of the corpus luteum (a hormone-secreting body in the women's reproductive system) and ending with either pregnancy or its degradation. If your luteal phase is shorter than that, you're likely to have a short luteal phase (also known as a luteal phase defect) which may signal of the low progesterone levels in your body. To get a more true picture, it's necessary that you know the exact date of your ovulation.
(See the recommended aids: ovulation tests)
2) Low Luteal Phase Temperatures
Progesterone enhances a thyroid hormone function, heating up your body. Hence, your basal body temperature rises after ovulation occurs, and stays up until the day before your next period starts. If your temperature doesn't rise or stay up, then it's likely that you have a progesterone deficiency.
(See the recommended aids: ear thermometers)
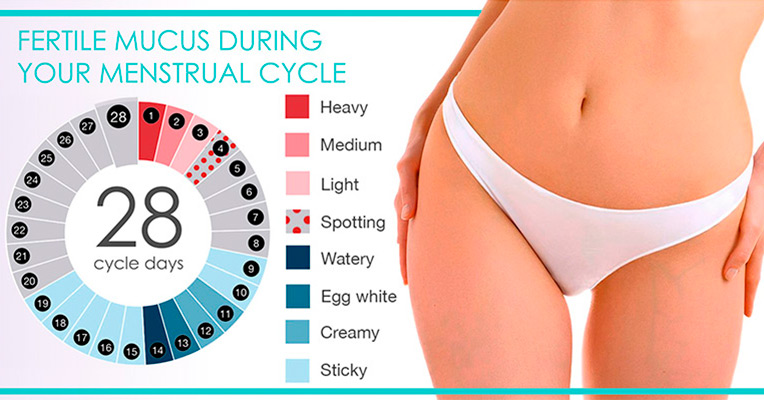
3) Fertile Mucus During Your Luteal Phase
Estrogen stimulates the production of clear and stretchy fertile mucus (a fluid secreted by the cervix). Progesterone dries cervical mucus up after ovulation. If progesterone levels are enough, you will have tackier, drier mucus throughout your luteal stage. If you see abundant cervical mucus in your luteal stage, it means that your progesterone levels have lowered. To get more detailed information on the amount of progesterone in your body, using progesterone test strips is advised.
(See the recommended aids: MFB Fertility 7 Urine Progesterone Test Strips)
4) Premenstrual Spotting
If you wonder whether low progesterone can cause spotting, the answer is yes, it can. Low levels of progesterone in feminine often lead to the occurrence of a small amount of red-brown spotting 3-4 days earlier than the period starts. Spotting can also appear as a result of some other health issues like gynecologic infections, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and uterine polyps. Therefore, you should go consult your doctor to find out the causes of premenstrual spotting and treat the problem right.
Causes of Low Progesterone
Identifying the causes for low progesterone is essential to treat the condition. Here are 5 most common reasons that may cause a progesterone deficiency:
- High Estrogen
Estrogen and progesterone are female hormones that work to balance each other in the body. When estrogen levels rise for whatever reason, it may cause a drop in progesterone levels. As a result, elevated levels of estrogen suppress progesterone production.
- Lack of Physical Activity and Unhealthy Nutrition
A balanced diet and regular exercise play a key role in progesterone production.Hormone-producing glands in the body tend to become dormant and stop producing progesterone. Lack of physical activity and poor diet lead to increased risk of obesity, excess estrogen, and lower progesterone production.
- Insulin Resistance
This is a pathological condition when the body is not capable to effectively use the insulin it produces. When glucose levels in the blood become either too low or too high, cells are unable to absorb progesterone. Moreover, anything that leads to spikes in insulin levels, namely refined carbohydrates, and sugars, may cause a drop in progesterone levels. Insulin resistance may coexist with obesity, diabetes, or polycystic ovarian syndrome.
- Chronic Stress
Chronic stress stimulates increased production of cortisol, a major stress hormone, decreasing the levels of progesterone. When cortisol levels keep high for an extended period of time, progesterone production is reduced.
- Medications
Some medication, like hormonal therapies and steroids, can affect progesterone levels. Besides, many oral contraceptives work by lowering progesterone levels to prevent an unplanned pregnancy. Certain medications may block the body's ability to effectively absorb progesterone.
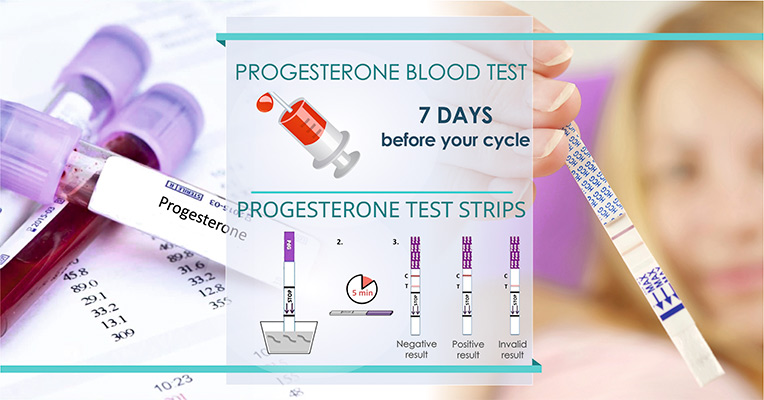
Get a Progesterone Test to Confirm Your Progesterone Is Low
If you think that you’ve got the signs of low progesterone, besides a progesterone test you may need to get a blood test to confirm whether your conjecture was right or not. For accurate progesterone test results, the blood test ought to be done approximately 7 days before your cycle. The minimum progesterone level should be higher than 1 ng/mL during your ovulation period. If the progesterone levels appear to be low, the first thing you need to do is see your doctor because self-diagnosing will not give you the true picture.
(See the recommended aids: progesterone tests)
What Are Normal Progesterone Levels?
So, what’s the normal level of progesterone in women? For those who don’t plan pregnancy, the levels of progesterone usually vary within the range of 0.2-1 ng/ml before they start ovulating and 5 ng/ml and higher after the ovulation period. During the luteal phase, progesterone levels tend to rise more and may reach 200 ng/ml if pregnancy occurs. Maintaining the high amount of progesterone in blood during pregnancy is important up to the term when a baby is born. Women with low progesterone levels during pregnancy are often prescribed progesterone supplements to prevent a miscarriage. If you aren’t pregnant but progesterone has risen significantly, it’s critical to go consult your doctor. For men, children, and women of postmenopausal age, the normal progesterone level is low and shouldn’t be higher than that of women during a premenstrual phase.
How to Deal With Low Progesterone Symptoms?
A low progesterone treatment usually consists of several cycles and involves a hormone therapy for improving the balance of estrogen and progesterone levels in women. Women needing the aid during the first trimester of pregnancy are often prescribed intramuscular injections which are typically made by mixing progesterone with one of the following oils: Ethyl Oleate, Olive Oil, Sesame Oil, Peanut and Cottonseed Oils. The compounds with these oils vary by thickness and the way they are absorbed into the muscle. Interestingly enough, the feedback from different women shows that different oils affect them differently and often result in very opposite reactions. Progesterone oils can also be massaged into the skin.
(See the recommended aids: Progestelle Progesterone Oil)
Progesterone is also used in the form of the pills and can be prescribed as a birth control or hormone balance treatment. Depending on the age of a woman, the symptoms, her body chemistry and the issues, the doctor will prescribe just the needed amount of progesterone to prevent overdose. Make sure to tell your doctor about the medicines you take (if you do any), and other health conditions to avoid allergic reactions and unpleasant side effects. Like any other health condition, hormone imbalance is a serious issue and ought to be treated under strict medical supervision.
Boost Your Progesterone Levels in a Natural Way
Some remedies, however, can be done. Women with progesterone deficiency should eat more food that contains zinc, selenium, magnesium, and different herbal medicines, take vitamin supplements, especially vitamins B and C and have a lot of rest to be able to deal with factors that cause stress and reduce progesterone levels. Maintaining a proper hygiene in the intimate zone is also important. Menstrual cups will provide leak-free protection so that you could feel confident in any situation. Besides, gynecologists don't recommend using perfumed gels or soaps since they can disrupt your natural vaginal flora. So, you can use a naturally-scented Castile soap to maintain pH balance of your intimate area.
(See the recommended aids: Castile soap, menstrual cups)